The Annuity Formula for the Present and Future Value of Annuities
The best way to demonstrate the strengths of the annuity calculator is to take some annuity examples. PV (along with FV, I/Y, N, and PMT) is an important element in the time value of money, which forms the backbone of finance. There can be no such things as mortgages, auto loans, or credit cards without PV. Present Value, or PV, is defined as the value in the present of a sum of money, in contrast to a different value it will have in the future due to it being invested and compound at a certain rate.
Ask Any Financial Question
If you want to compute today’s present value of a single lump sum payment (instead of series of payments) in the future than try our present value calculator here. The value today of a series of equal payments or receipts to be made or received on specified future dates is called the present value of an annuity. The present value of an annuity refers to how much money would be needed today to fund a series of future annuity payments. Or, put another way, it’s the sum that must be invested now to guarantee a desired payment in the future. In contrast to the FV calculation, PV calculation tells you how much money would be required now to produce a series of payments in the future, again assuming a set interest rate. As you might imagine, the future value of an annuity refers to the value of your investment in the future, perhaps 10 years from today, based on your regular payments and the projected growth rate of your money.
How to Calculate the Future Value of an Annuity
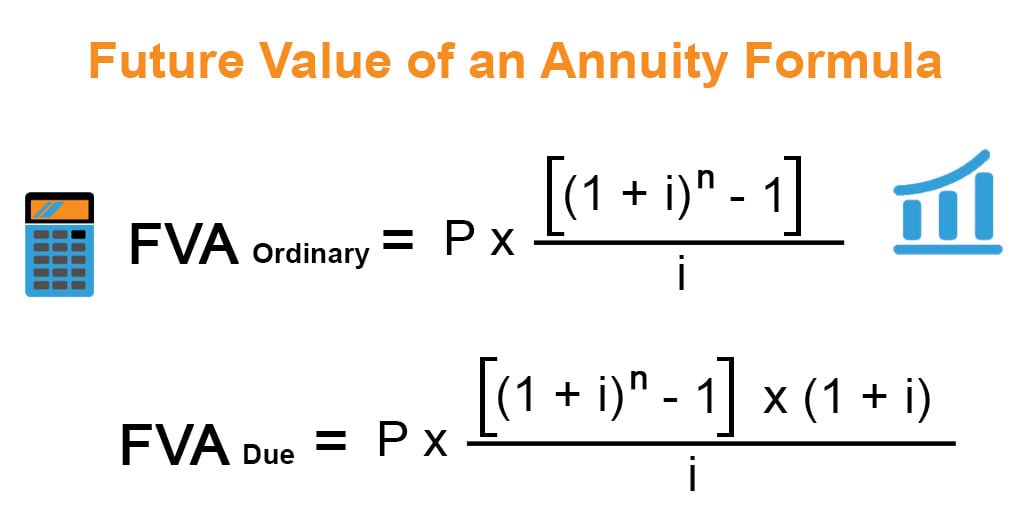
To put it simply, any financial product that involves a series of payments made at equal intervals is an annuity. The series of payments can be either deposits (with positive signs) or withdrawal (with negative signs). Therefore, if you make regular deposits into a savings account, monthly home mortgage, monthly insurance account or pension plan, you happen to face an annuity. The three constant variables are the cash flow at the first period, rate of return, and number of periods. The formulas described above make it possible—and relatively easy, if you don’t mind the math—to determine the present or future value of either an ordinary annuity or an annuity due. Such calculations and their results can add confidence to your financial planning and investment decision-making.
What’s the Difference Between the Present Value and Future Value?
This calculator will calculate the present value of an annuity starting with either a future lump sum, or with a future payment amount. The internal rate of return (IRR calculator) of a project is such a discount rate at which the NPV equals zero. In other words, the company will neither earn nor lose on such a project – the gains are equal to costs. There are many different types of annuities, including tax-advantaged annuities, fixed or variable rate annuities, annuities that pay out a death benefit to families or last a lifetime, and more.
It’s important to note that the discount rate used in the present value calculation is not the same as the interest rate that may be applied to the payments in the annuity. The discount rate reflects the time value of money, while the interest rate applied to the annuity payments reflects the cost of borrowing or the return earned on the investment. For example, if an individual could earn a 5% return by investing in a high-quality corporate bond, they might use a 5% discount rate when calculating the present value of an annuity. The smallest discount rate used in these calculations is the risk-free rate of return.
Recommended Finance Resources
The dollar received at the end of year 3 must be discounted back 3 periods; the dollar received at the end of year 2 must be discounted back 2 periods; and so forth. The present value of an annuity refers to the present value of a series of future promises to pay or receive an annuity at a specified interest rate. Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, so the person would come out ahead by choosing the lump-sum payment over the annuity.
You can solve for all four variables involved in present value of annuity calculation viz. Unlike spreadsheets and financial calculator models, there is no convention of using negative numbers. When calculating the present summary of federal tax law changes for 2010 value of an annuity payment, a specific formula is used, based on the three assumptions above. Annuities usually defer taxes on investment gains but then tax withdrawals from the annuity at ordinary income rates.
- First enter the amount of the payment that you’ve been making, the account’s interest rate, the number of years you’ve been making these deposits, and the payment interval.
- To learn more about or do calculations on future value instead, feel free to pop on over to our Future Value Calculator.
- In general, the shorter an annuity is owned, the higher the surrender fee.
- For example, you can buy an annuity that requires a single upfront payment, or a series of payments to the insurance company.
- You can use this calculator to calculate loan repayments and payouts from immediate insurance schemes.
Regardless, it is clear that an annuity investment—independent of your personal level of risk tolerance—can be a very lucrative investment. However, there are things to consider when deciding whether an annuity investment will make financial sense for you. Assuming that the term is 5 years and the interest rate is 7%, the present value of the annuity is $315,927.28. Use this calculator to find the present value of annuities due, ordinary regular annuities, growing annuities and perpetuities.
You can calculate the present or future value for an ordinary annuity or an annuity due using the formulas shown below. There are several ways to measure the cost of making such payments or what they’re ultimately worth. Read on to learn how to calculate the present value (PV) or future value (FV) of an annuity.
This is because cash received in the future is not as valuable as cash received today. Present value tells you how much money you would need now to produce a series of payments in the future, assuming a set interest rate. An ordinary annuity is a series of recurring payments that are made at the end of a period, such as payments for quarterly stock dividends.
In general, the shorter an annuity is owned, the higher the surrender fee. As an example, if an annuity contract has an eight-year surrender period, it’s quite possible to have to pay eight percent of the value of the investment if it is surrendered within the first year. When surrendering annuities, other penalties may also be applied, such as a 10% IRS penalty. What’s more, you can analyze the result by following the progress of balances in the dynamic chart or the annuity table. For example, you can use it either for regular deposits or withdrawals, for multiple frequencies, or you can compare ordinary annuity vs. annuity due. Annuities are financial assets that promise investors a guaranteed future return in exchange for making an investment today.

۰ دیدگاه